12 Nov 2024 11:31:10 am
Tags : Baku
Topic: Places in news
Why in the news?
Source: Down To Earth
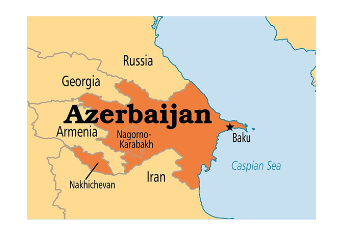
About Baku:
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC):
0 Comments

© 2026 Catalyst IAS All Rights Reserved.